Google’s CEO Sundar Pichai says it’s only a matter of time until we’ll all be liberated from our smartphones. His company is envisioning a future in which we interact with a far more advanced form of artificial intelligence. It didn’t take long for me to realise that I had reached Google land. Exactly two minutes after arriving in Mountain View, Northern California, one of the many boomtowns that make up Silicon Valley, I spotted my first driverless car. It was a little white pod with dashes of bright colour painted on its side, making its way along the highway in the evening rush hour, ignored by blasé commuters.
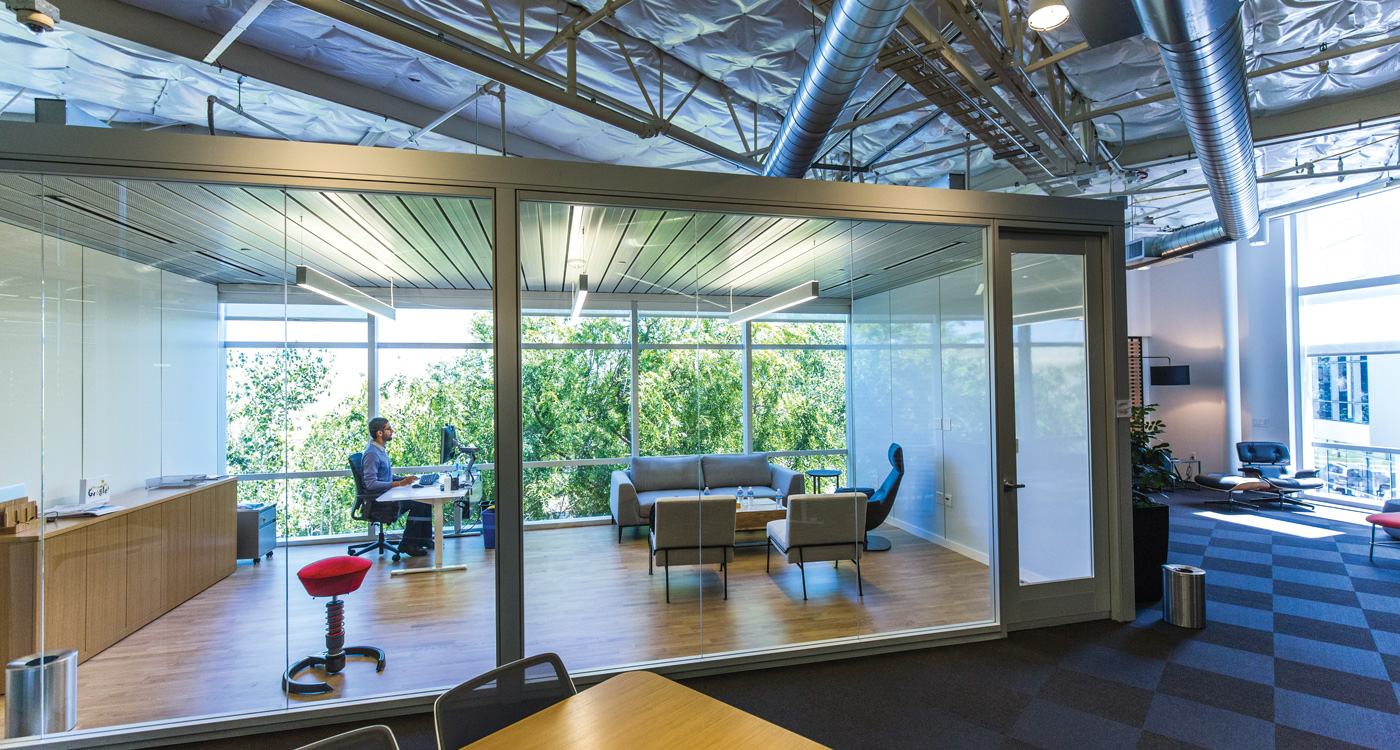
Everything at Google HQ, home of the search engine, YouTube, Android and much else besides, is exactly the way you would expect it to be. A sprawling network of leafy low-rise offices on the edge of the California wilderness, it looks and feels more like a university campus than the offices of one of the world’s most powerful corporations. The complex is so large that one needs a map to find one’s way around; the ultra-casually dressed, hyper-educated young staff hail from all over the world.
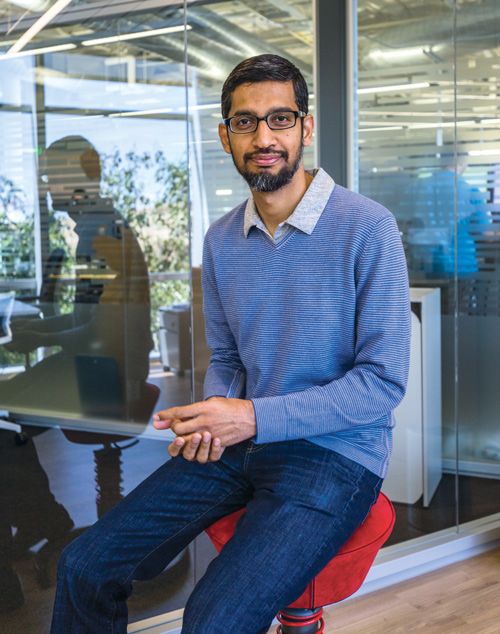
The man charged with ensuring that the firm stays on track is Sundar Pichai, Google’s chief executive. A sprightly, slightly unassuming 43-year old from Southern India, he is one of the Valley’s hottest stars; he has been in the role for almost a year. He reports to Larry Page and Sergey Brin, Google’s co-founders who now run Alphabet, the overall holding company that also invests in ventures such as glucose-sensing contact lenses, longevity research and automated vehicles.

WE’VE BEEN MAKING VERY MEANINGFUL PROGRESS IN MACHINE LEARNING AND ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. THE RATE HAS REACHED AN INFLECTION POINT.
Pichai is living the American Dream: when in the 1990s he won a scholarship to Stanford, the world’s top tech university in California, his one-way ticket from India cost more than his father’s annual salary. Dressed in a shirt and jeans, his accent part-Indian and part-American, his mission is clear: he wants people to stop thinking about Google primarily as a means of searching for publicly available information but as a full-on “assistant”, helping people to live their lives in all sorts of ways.
In addition to further refining and advancing his core products, he is targeting the home and the car as Google’s next frontiers. Crucially, he wants to liberate us from having to rely on computers and phones when interacting with his company. He would like us to be able to talk to our house or car, instructing Google to order some takeaway, asking it what the temperature will be in Ibiza next week, requesting an item be added to the family diary or shopping list and then be reminded that it’s time for that medical appointment.
The world is only just getting used to the smartphone revolution, but the bespectacled Pichai is already thinking “post-mobile”. “Today, we pull out a black rectangular piece of something. It’s much better than what’s been before, but it’s still a physical device with which we interact,” he says. But as we move away from this, “over time the experience will become much more intuitive, much more natural.”

PHOTOGRAPHER: Brooks Kraft
Teaching computers to understand casual, contextual conversation in every language and accent is key to this quest to normalise our interactions with computers and to place Google even more squarely at the centre of our lives. Achieving this would require solving complex computational problems, and Google is investing vast amounts in machine learning – a form of artificial intelligence (AI). This is central to the company’s long-term future; it permeates everything it now does.
It’s no longer enough to program machines with all the answers or to rely on traditional statistical analysis to allow them to work out what’s what – instead, the firm now relies on techniques such as neural networks that allow computers to teach themselves by sifting through massive amounts of data, learning from patterns, regularities and interconnections.
The potential is massive, Pichai believes. “We’ve been making very meaningful progress in machine learning and AI. The rate has reached an inflection point.” To some, Google’s strategy will seem terrifying: won’t artificial intelligence end up automating all jobs, and, in extremis, lead to a Terminator-style dystopia where machines take control?
The Google boss believes that the benefits of harnessing AI will be much greater than the costs and that the changes will take decades, allowing societies to adapt. New professions will continue to be created, replacing jobs that are automated. He does think, however, that over time society will come up with a new social contract to deal with the changes.
“Technology is always disruptive. But it’s a force for making people’s lives better. It’s also an incredibly democratising force over time.” AI will be transformative he believes, and not just in his company’s own area. Take medicine. He recounts that “just in the last months, we’ve seen some young people in Google diagnosed with cancer. It’s shocking to see. I look at that and I think: can machine learning and artificial intelligence make progress on these things? In my mind, the answer is yes. We are in such early stages. It’s imperative that we bring this to the world.”
He also believes that his “assistant” project, and the progress of artificial intelligence, will make it easier to protect privacy, another controversial area for the tech industry. “Today’s software is difficult. You want to give users lots of privacy controls but then it becomes clunky and unstable. You still need to go to a settings page. It needs to be much more intuitive.”
He foresees a day when users will simply speak to a device to change their privacy settings, and his digital assistant will behave more and more like human beings, modifying how much personal information is divulged depending on context, on whether one is at work or at home, alone or in company.
But while the future seen from Mountain View is extraordinarily exciting, plenty of entrepreneurs from around the world would love to make it their own. How much does he worry about the competition and the possibility that upstart firms could eventually displace Google? “A lot. It never feels for a moment that we are a large successful company. That’s not what it feels like. I feel that every year you need to earn your next year’s success.”
The most obvious way to achieve this is to try and keep true to its start-up roots. “I awake everyday and say: how do [we make sure our] people feel that they are a small company, scrappy, frugal, disciplined? In technology, you often solve problems because you have constraints, because you don’t have money. So you think of a different way. Technology has always been reshaped by small companies with an ability to move fast and do things differently.”
The key is to nurture bottom-up initiatives. Google allows its staff to dedicate 20 per cent of their time to interesting projects: that’s how it invented Cardboard, a cheap way of enjoying virtual reality. One of its core products, the Android operating system that now powers so many devices, is open source.
Unlike Apple’s rival system, anybody can use it. This has helped make it hugely successful but is also reducing the barriers to entry for competitors. “All the work we have done on Android makes it even easier for [a competitor] to create something. Amazon has just announced two new phones, built on Android”.
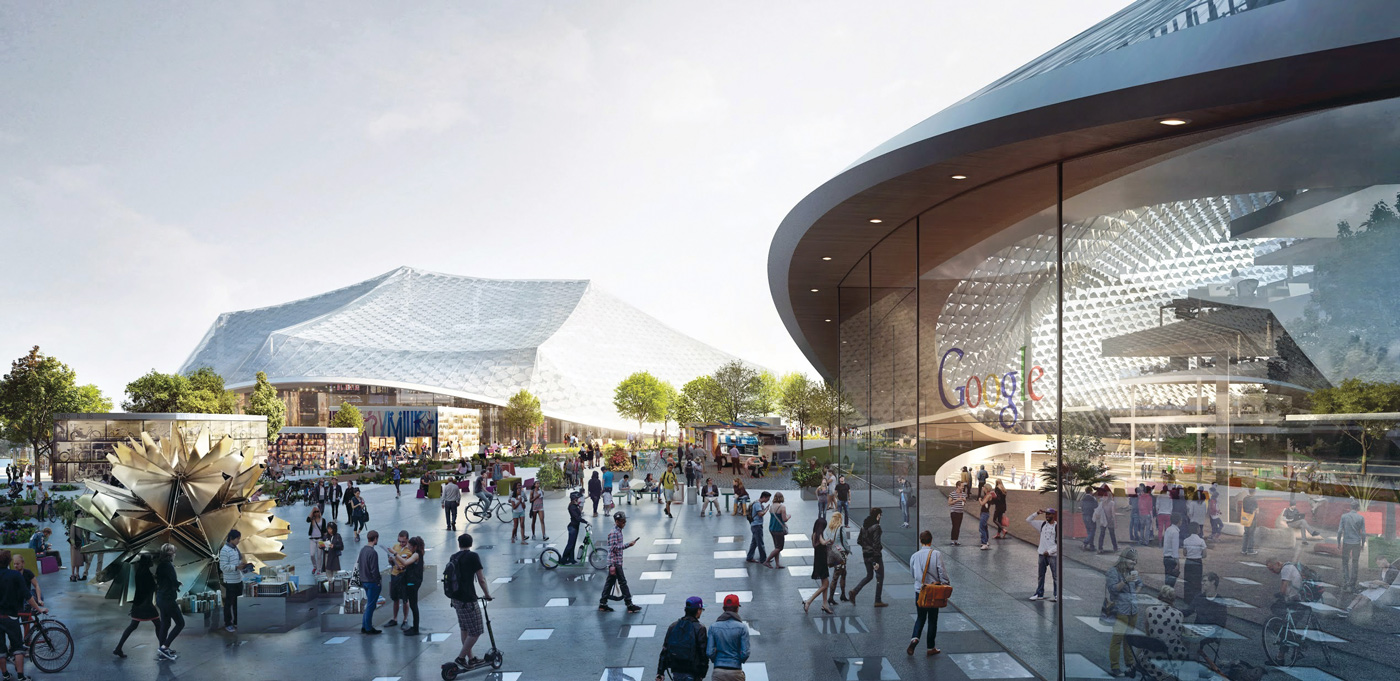

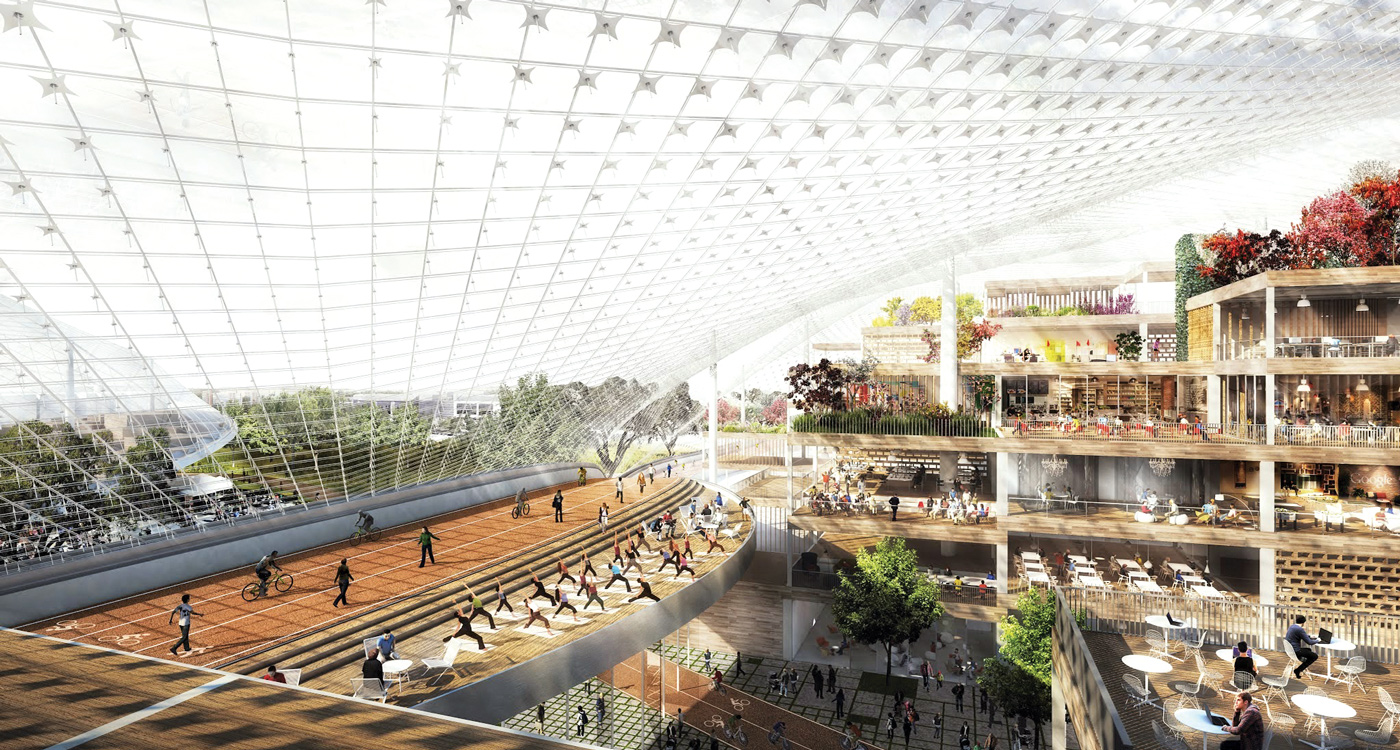
Google’s HQ in California, previously occupied by Silicon Graphics (SGI), is undergoing an ambitious expansion due for completion in 2019. The ‘Charleston East’ complex will include campus rooms divided up into rectilinear ‘pavilions’ sheltered beneath a tented photovoltaic roof canopy.
It is not surprising, therefore, that Pichai disagrees with Brussels’ competition commissioners, who worry his firm has too much market power. One of their arguments is that Google pre-installs too many apps on its devices and that this makes it hard for competing app makers to break in.
The Google boss argues that he is simply ensuring that devices are ready to use and come fully loaded with essential tools, such as maps: “We think about what the services are that are used by a lot of people, and we put them in. We then give users the choice to do whatever else they want. When you press factory reset on that phone, it needs to work.”
Google’s vast size has downsides – both cultural and political – but it also allows it to spend billions on projects that have a very long-term and uncertain payoff. “Because we are a large company, we can think for the very long-term. We take on projects without knowing the business model”, Pichai explains.
In addition to his attempt at turning Google into an assistant service, creating a personalised service for every human being, the company is continuing to take on TV companies. Its YouTube unit is now colonising the living room, grabbing ever more market share and delivering a remarkably engaged audience for advertisers. The firm has started to commission its first original content from its home-grown YouTube superstars, some of whom are better known to youngsters than Hollywood names, and has launched a subscription service.
Its live broadcasts are taking off. Not everything Google does pays off: it’s Glass product – a transparent, wearable screen that looked like a digital mask – bombed. The competition is intensifying on all fronts, including from digital “walled gardens” such as Facebook, an increasingly powerful player. But only a fool would bet against Sundar Pichai, his team of super-bright lieutenants and their armies of maths geniuses. The revolution is on track, it will keep changing the way we live, and it will be orchestrated, at least in part, from a giant suburban business park in Silicon Valley.